Welding Processes
COC offers comprehensive training in the following Welding Processes:
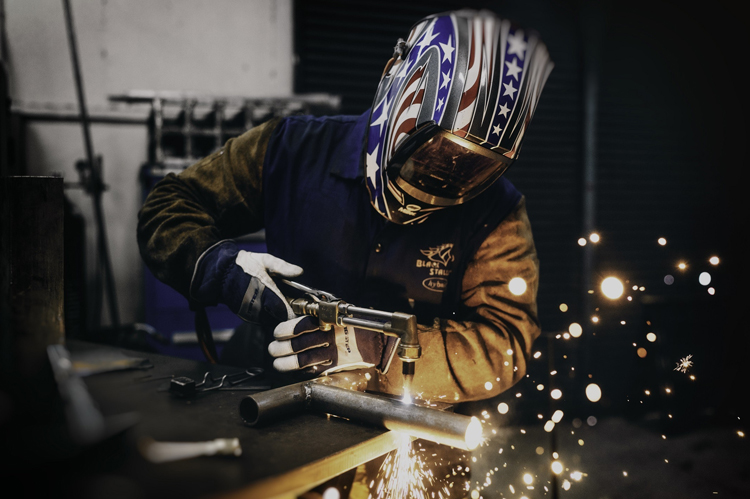
Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
An arc welding process that produces a coalescence of metals by heating them with an arc between a flux covered metal electrode and the workpieces. Shielding is obtained from the breakdown of the electrode flux covering during the welding operation.
Industry applications:
- Structural Steel
- Pipe Welding and Fabrication
- Maintenance and Repair

Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW)
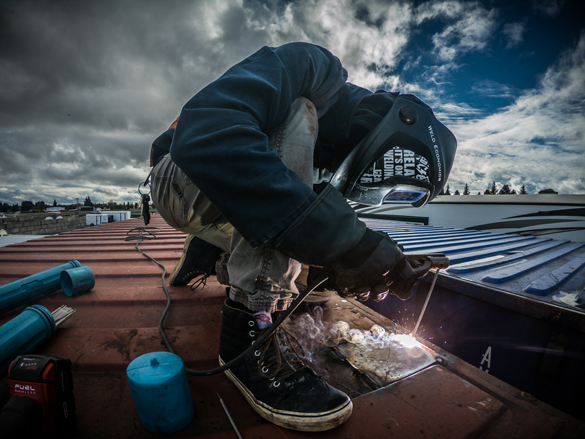
Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
An arc welding process that produces coalescence of metal by heating them with an arc between a continuous filler metal electrode and the workpeices. Shielding is provided by a flux contained within the tubular electrode. Additional shielding may or may not be obtained from an externally supplied gas or gas mixture.
Industry applications:
- Structural Steel
- Pipe Welding and Fabrication

Flux Cored Arc Welding (FCAW)
Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Arc welding process that produces coalescence of metal by heating them with an arc between a continuous filler metal electrode and the workpieces. Shielding is obtained entirely from an externally supplied gas.
Industry applications:
- Light Gauge Fabrication
- Auto Body
- Sheet Metal
- Motorsports
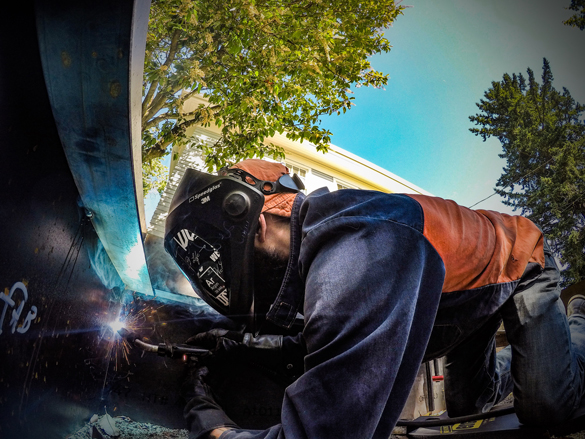

Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW)
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW)
Gas tungsten arc welding, also known as tungsten inert gas welding, is an arc welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to produce the weld. The weld area and electrode are protected from oxidation or other atmospheric contamination by an inert shielding gas.
Industry applications:
- Light Gauge Fabrication
- Auto Body
- Sheet Metal
- Motorsports
Gas Tungstaen Arc Welding (GTAW)
Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
A welding process that produces coalescence of materials by heating, with the heat obtained from the application of a concentrated coherent light beam focused into the joint.
Industry applications:
- Medical Device Manufacture
- Aerospace
- Automotive Manufacturers
- Mold Repair
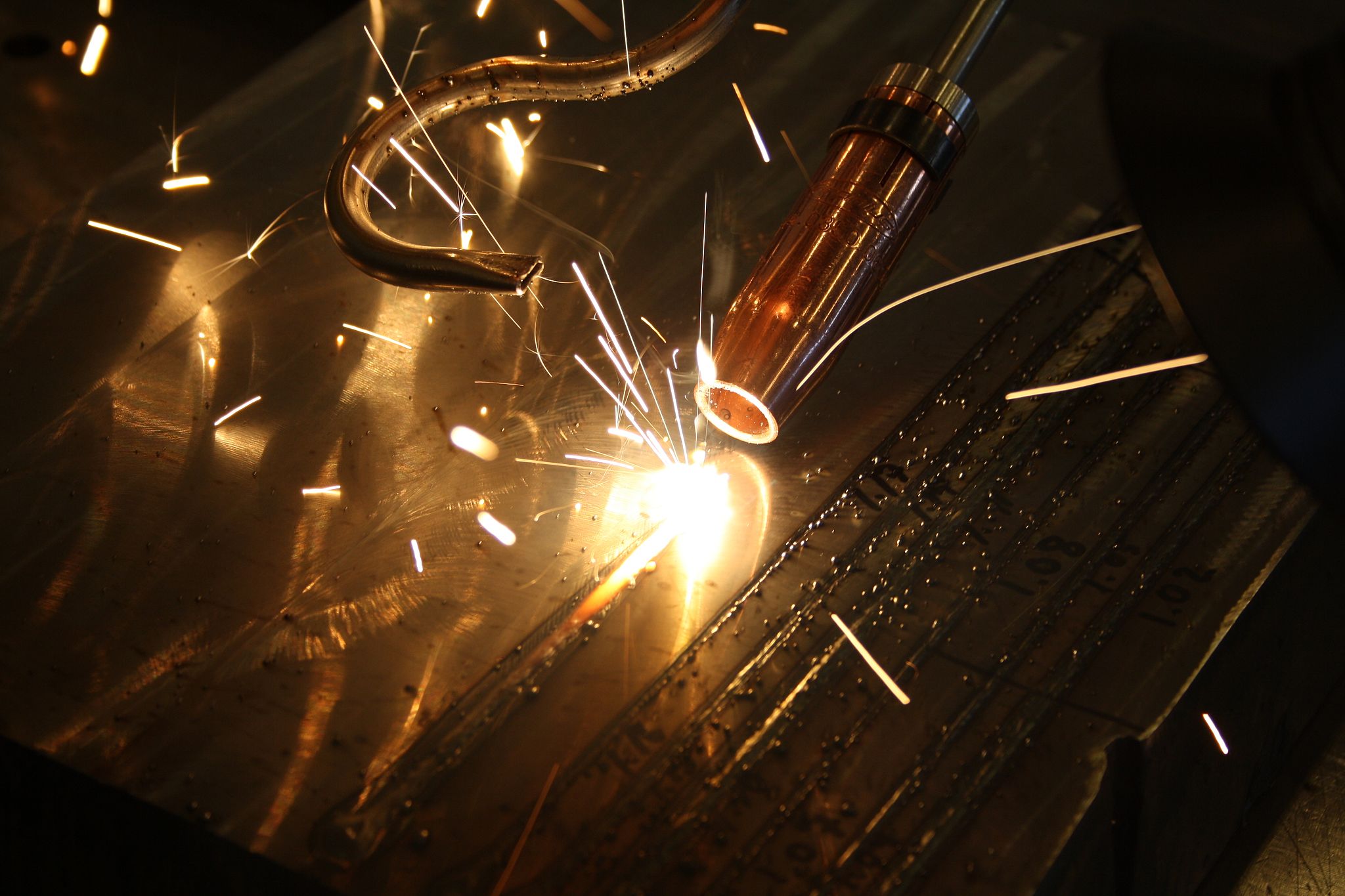

Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
Robotic Gas Metal Arc Welding (Robotic GMAW)
In robotic gas welding therobot controller operates the entire robotic system. This includes the welding equipment.
All desired robotic movements are programmed and stored by using a teach pendant. Once the program is finalized, robotic operation is initiated via the start button on the controller.
As in manual gas metal arc welding, an electric arc between a continuously fed metal electrode and the base metal produces heat melting the base metal and the electrode, creating the weld.
Industry applications:
- Automotive Manufacture
- Production Structural Steel
- Light Steel Fabrication Prodcution
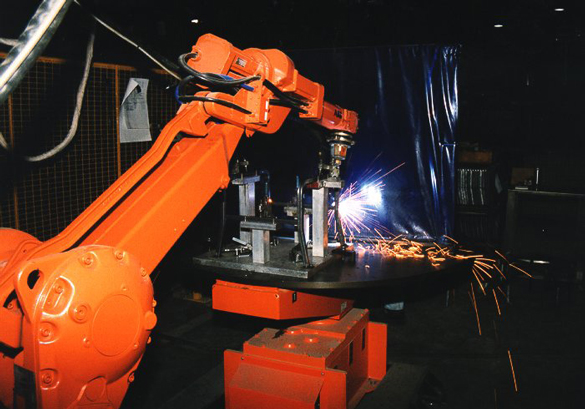

Robotic Gas Metal Arc Welding (Robotic GMAW)

 My Canyons
My Canyons  Canvas
Canvas 
